Am I Losing My Hearing?
Untreated hearing loss can be frustrating and isolating. According to a study by the National Council on Aging, people with untreated hearing loss were more likely to report depression and anxiety, and participate less in social activities than those who wear hearing aids.
Possible signs of hearing loss:
- Do you frequently miss words when people are speaking?
- Do you ask people to repeat themselves?
- Do others tell you your TV or radio is to loud?
- Do/Have you work(ed) in a noisy environment?
- Do you have a ringing or buzzing in your ears?
- Do you ever experience dizziness?
- Have others told you they think you have a hearing problem?
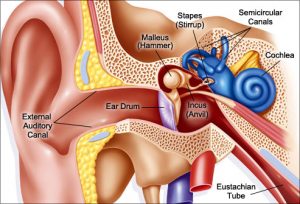
Three types of hearing loss. Hearing loss affects people of all ages and can be caused by many different factors. The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss. Here are facts that patients should know about each type:
- Sensorineural – This type of hearing loss occurs when the inner ear or the actual hearing nerve itself becomes damaged. This loss generally occurs when some of the hair cells within the cochlea are damaged. Sensorineural loss is the most common type of hearing loss. It can be a result of aging, exposure to loud noise, injury, disease, certain drugs or an inherited condition. This type of hearing loss is typically not medically or surgically treatable; however, many people with this type of loss find that hearing aids can be beneficial.
- Hearing deterioration of the inner ear (nerves)
- Possible causes are aging, noise exposure, or illness
-
Conductive – This type of hearing loss occurs in the outer or middle ear where sound waves are not able to carry all the way through to the inner ear. Sound may be blocked by earwax or a foreign object located in the ear canal; the middle ear space may be impacted with fluid, infection or a bone abnormality; or the eardrum may have been injured. In some people, conductive hearing loss may be reversed through medical or surgical intervention. In children, conductive hearing loss is most common with recurrent ear infections or insertion of foreign objects into their ear canal.
- Hearing deterioration of the middle and inner ear (bones, eardrum, membrane)
- Possible causes are traumatic injury, tumors, fluid in the middle ear, exposure to loud noise, foreign objects, wax buildup
- Mixed – Sometimes people can have a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. They may have a sensorineural hearing loss and then develop a conductive component in addition, i.e. age-related hearing loss with a wax-blocked ear canal.
- Combination of Sensorineural and Conductive hearing loss
- Hearing testing is critical for discovering exactly what type of hearing loss you have, and will help determine the hearing care solution that is right for you.
Source: John Hopkins Health Library
Human interaction is one of the most valuable resources we take for granted. Hearing loss doesn’t just affect those individuals suffering from hearing loss, it has the compounding effect of ADVERSELY IMPACTING THE LIVES OF EVERYONE THEY LOVE.
Hearing Loss by the Numbers
Number of Americans reporting some degree of hearing loss
%
American children aged 6 through 19 with some degree of hearing loss
Children born in the United States with a detectable hearing loss in one or both ears
- Ages 45-54 2%
- Ages 55-64 8.5%
- Ages 65-74 25%
- Ages 75 and over 50%
American adults with DISABLING hearing loss